Deploy jobs
You can use deploy jobs to build production data assets. Deploy jobs make it easy to run dbt commands against a project in your cloud data platform, triggered either by schedule or events. Each job run in dbt Cloud will have an entry in the job's run history and a detailed run overview, which provides you with:
- Job trigger type
- Commit SHA
- Environment name
- Sources and documentation info, if applicable
- Job run details, including run timing, model timing data, and artifacts
- Detailed run steps with logs and their run step statuses
You can create a deploy job and configure it to run on scheduled days and times or enter a custom cron schedule.
Prerequisites
- You must have a dbt Cloud account and Developer seat license.
- For the Trigger on job completion feature, your dbt Cloud account must be on the Team or Enterprise plan.
- You must have a dbt project connected to a data platform.
- You must have access permission to view, create, modify, or run jobs.
- You must set up a deployment environment.
Create and schedule jobs
- On your deployment environment page, click Create job > Deploy job to create a new deploy job.
- Options in the Job settings section:
- Job name — Specify the name for the deploy job. For example,
Daily build. - (Optional) Description — Provide a description of what the job does (for example, what the job consumes and what the job produces).
- Environment — By default, it’s set to the deployment environment you created the deploy job from.
- Job name — Specify the name for the deploy job. For example,
- Options in the Execution settings section:
- Commands — By default, it includes the
dbt buildcommand. Click Add command to add more commands that you want to be invoked when the job runs. - Generate docs on run — Enable this option if you want to generate project docs when this deploy job runs.
- Run source freshness — Enable this option to invoke the
dbt source freshnesscommand before running the deploy job. Refer to Source freshness for more details.
- Commands — By default, it includes the
- Options in the Triggers section:
- Run on schedule — Run the deploy job on a set schedule.
- Timing — Specify whether to schedule the deploy job using Intervals that run the job every specified number of hours, Specific hours that run the job at specific times of day, or Cron schedule that run the job specified using cron syntax.
- Days of the week — By default, it’s set to every day when Intervals or Specific hours is chosen for Timing.
- Run when another job finishes — Run the deploy job when another upstream deploy job completes.
- Project — Specify the parent project that has that upstream deploy job.
- Job — Specify the upstream deploy job.
- Completes on — Select the job run status(es) that will enqueue the deploy job.
- Run on schedule — Run the deploy job on a set schedule.
-
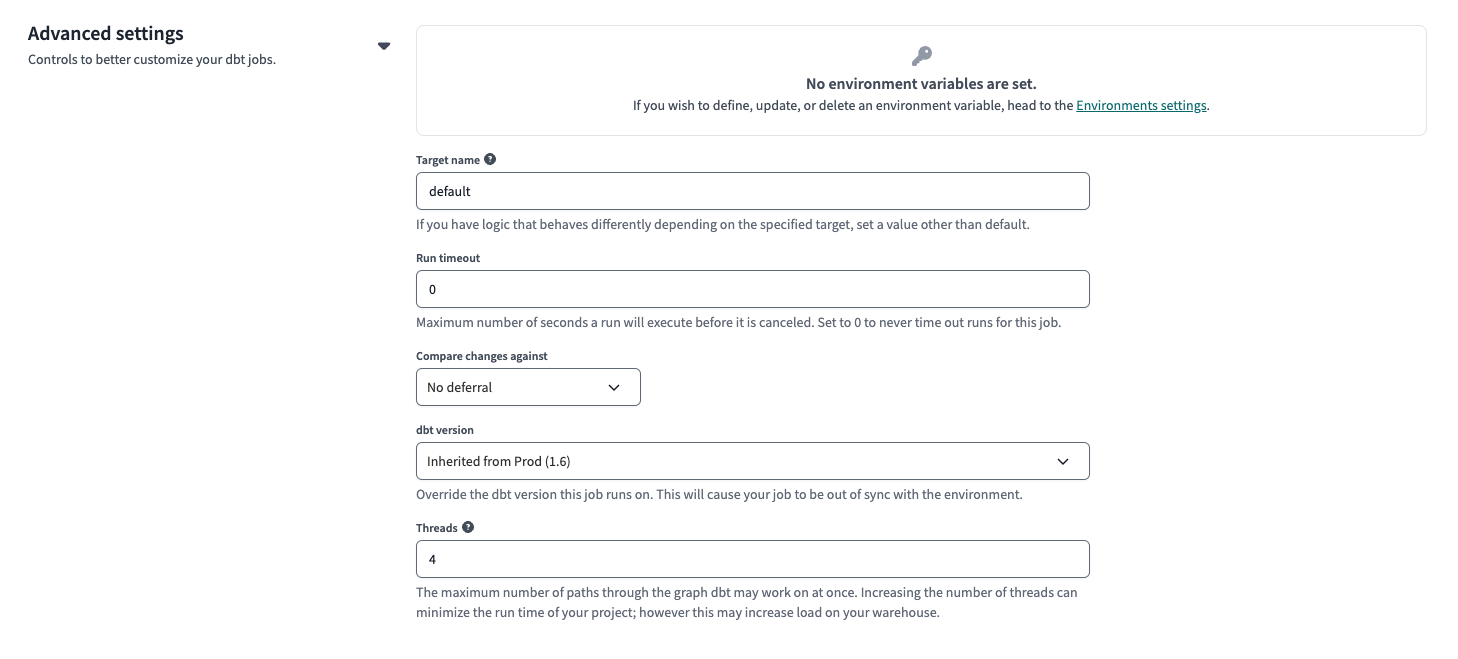
(Optional) Options in the Advanced settings section:
- Environment variables — Define environment variables to customize the behavior of your project when the deploy job runs.
- Target name — Define the target name to customize the behavior of your project when the deploy job runs. Environment variables and target names are often used interchangeably.
- Run timeout — Cancel the deploy job if the run time exceeds the timeout value.
- Compare changes against — By default, it’s set to No deferral. Select either Environment or This Job to let dbt Cloud know what it should compare the changes against.
infoOlder versions of dbt Cloud only allow you to defer to a specific job instead of an environment. Deferral to a job compares state against the project code that was run in the deferred job's last successful run. While deferral to an environment is more efficient as dbt Cloud will compare against the project representation (which is stored in the
manifest.json) of the last successful deploy job run that executed in the deferred environment. By considering all deploy jobs that run in the deferred environment, dbt Cloud will get a more accurate, latest project representation state.- dbt version — By default, it’s set to inherit the dbt version from the environment. dbt Labs strongly recommends that you don't change the default setting. This option to change the version at the job level is useful only when you upgrade a project to the next dbt version; otherwise, mismatched versions between the environment and job can lead to confusing behavior.
- Threads — By default, it’s set to 4 threads. Increase the thread count to increase model execution concurrency.
Schedule days
To set your job's schedule, use the Run on schedule option to choose specific days of the week, and select customized hours or intervals.
Under Timing, you can either use regular intervals for jobs that need to run frequently throughout the day or customizable hours for jobs that need to run at specific times:
-
Intervals — Use this option to set how often your job runs, in hours. For example, if you choose Every 2 hours, the job will run every 2 hours from midnight UTC. This doesn't mean that it will run at exactly midnight UTC. However, subsequent runs will always be run with the same amount of time between them. For example, if the previous scheduled pipeline ran at 00:04 UTC, the next run will be at 02:04 UTC. This option is useful if you need to run jobs multiple times per day at regular intervals.
-
Specific hours — Use this option to set specific times when your job should run. You can enter a comma-separated list of hours (in UTC) when you want the job to run. For example, if you set it to
0,12,23,the job will run at midnight, noon, and 11 PM UTC. Job runs will always be consistent between both hours and days, so if your job runs at 00:05, 12:05, and 23:05 UTC, it will run at these same hours each day. This option is useful if you want your jobs to run at specific times of day and don't need them to run more frequently than once a day.
dbt Cloud uses Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) and does not account for translations to your specific timezone or take into consideration daylight savings time. For example:
- 0 means 12am (midnight) UTC
- 12 means 12pm (afternoon) UTC
- 23 means 11pm UTC
Cron schedule
To fully customize the scheduling of your job, choose the Cron schedule option and use cron syntax. With this syntax, you can specify the minute, hour, day of the month, month, and day of the week, allowing you to set up complex schedules like running a job on the first Monday of each month.
Cron frequency
To enhance performance, job scheduling frequencies vary by dbt Cloud plan:
- Developer plans: dbt Cloud sets a minimum interval of every 10 minutes for scheduling jobs. This means scheduling jobs to run more frequently, or at less than 10 minute intervals, is not supported.
- Team and Enterprise plans: No restrictions on job execution frequency.
Examples
Use tools such as crontab.guru to generate the correct cron syntax. This tool allows you to input cron snippets and return their plain English translations. The dbt Cloud job scheduler supports using L to schedule jobs on the last day of the month.
Examples of cron job schedules:
0 * * * *: Every hour, at minute 0.*/5 * * * *: Every 5 minutes. (Not available on Developer plans)5 4 * * *: At exactly 4:05 AM UTC.30 */4 * * *: At minute 30 past every 4th hour (such as 4:30 AM, 8:30 AM, 12:30 PM, and so on, all UTC).0 0 */2 * *: At 12:00 AM (midnight) UTC every other day.0 0 * * 1: At midnight UTC every Monday.0 0 L * *: At 12:00 AM (midnight), on the last day of the month.0 0 L 1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9,10,11,12 *: At 12:00 AM, on the last day of the month, only in January, February, March, April, May, June, August, September, October, November, and December.0 0 L 7 *: At 12:00 AM, on the last day of the month, only in July.0 0 L * FRI,SAT: At 12:00 AM, on the last day of the month, and on Friday and Saturday.0 12 L * *: At 12:00 PM (afternoon), on the last day of the month.0 7 L * 5: At 07:00 AM, on the last day of the month, and on Friday.30 14 L * *: At 02:30 PM, on the last day of the month.
Trigger on job completion teamenterprise
To chain deploy jobs together, enable the Run when another job finishes option and specify the upstream (parent) job that, when it completes, will trigger your job. You can also use the Create Job API to do this.
You can set up a configuration where an upstream job triggers multiple downstream (child) jobs and jobs in other projects. You must have proper permissions to the project and job to configure the trigger.
For jobs that are triggered to run by another job, a link to the upstream job run is available from your job's run details.